BRICS countries
Table of Contents
-
Overview
-
- Introduction
-
- The BRICS Summit
-
- The BRICS countries
-
- The BRICS economies
-
- The BRICS Development Bank
-
- The BRICS Interbank Cooperation Mechanism
-
- The BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement
-
- The BRICS Post-2015 Development Agenda
-
- The BRICS in the global economy
-
- The future of the BRICS
-
References
Overview
The BRICS countries are a group of nations consisting of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. Formed in 2009, the group’s aim is to promote economic growth and financial stability throughout its member countries. The group has been successful in achieving its goals, with member countries’ economies growing at a faster rate than the global average. The BRICS countries are considered to be some of the most powerful and influential nations in the world.
- Introduction
The BRICS group of countries – Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – are important emerging markets with a combined population of over 3 billion people, or approximately 40% of the world’s population. They are also some of the fastest-growing economies in the world, with an average annual growth rate of 5.3% between 2010 and 2016.
The BRICS countries are diverse, with each country having its own unique strengths and challenges. However, they also have some commonalities, such as being members of the G20 group of major economies and being home to some of the world’s largest populations.
The BRICS countries are increasingly working together on economic, political and security issues. In 2009, they established the BRICS Forum, a platform for cooperation on economic and political issues. In 2014, they launched the New Development Bank, an institution that will finance infrastructure and sustainable development projects in the BRICS countries.
The BRICS countries are important players in the global economy and their cooperation is increasingly shaping the world’s economic and political landscape.
- The BRICS Summit
The BRICS Summit is an annual meeting of the leaders of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa, held to discuss issues of mutual interest. The first summit was held in 2009, and the most recent in 2018.
The summit is seen as a way for the leaders of the five countries to discuss issues of mutual concern and to work towards common goals. The leaders of the five countries have discussed a range of issues at the summit, including economic growth, trade, investment, and global governance.
The BRICS countries are some of the fastest-growing economies in the world, and the summit has been seen as a way to challenge the dominance of the developed world. The summit has been seen as a way to promote the interests of the BRICS countries and to increase their influence in the world.
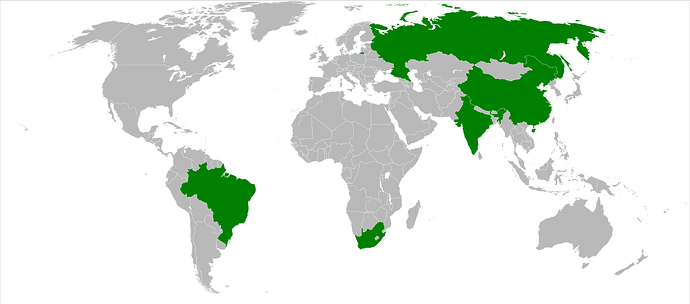
- The BRICS countries
The BRICS countries are the five emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. They are known as the BRICS nations.
The BRICS countries are united by their shared commitment to promote open and inclusive global economic growth, to safeguard global financial stability, and to advance international cooperation.
The BRICS countries are significant players in the global economy. Together, they account for over 40% of the world’s population, 30% of its landmass, and nearly 20% of its GDP.
The BRICS countries are committed to working together to build a more prosperous, equitable, and sustainable world for all.
- The BRICS economies
The BRICS economies are the five major emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. They are known as the BRICS nations. The BRICS countries are all members of the G20, and have been growing rapidly over the past few years.
The combined GDP of the BRICS economies was US$16.0 trillion in 2016, accounting for 20% of the global economy. The BRICS countries are also home to over 42% of the world’s population.
The BRICS economies are some of the most dynamic and fastest-growing in the world. Between 2010 and 2016, the combined GDP of the BRICS nations grew at an average annual rate of 7.0%. This is significantly faster than the global average of 3.7%.
China is the largest economy in the BRICS, with a GDP of US$11.2 trillion in 2016. It is followed by India (US$2.9 trillion), Brazil (US$2.1 trillion), Russia (US$1.3 trillion) and South Africa (US$0.6 trillion).
The BRICS nations are expected to continue to grow at a rapid pace in the coming years. China and India are forecast to be the two fastest-growing major economies in the world, with annual growth rates of 6.7% and 7.3% respectively between 2018 and 2020. Brazil, Russia and South Africa are also expected to see strong economic growth over this period.
- The BRICS Development Bank
The BRICS Development Bank is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS countries. The bank’s headquarters is in Shanghai, China. The bank’s main aim is to finance infrastructure projects in the BRICS countries.
The bank’s capital is US$100 billion, with equal contributions from each of the five member countries. The bank began operations in July 2015. The first president of the bank is K.V. Kamath, from India.
The bank has been seen as a rival to the Western-dominated World Bank and International Monetary Fund. Some have seen the establishment of the bank as a sign of the growing economic clout of the BRICS countries.
- The BRICS Interbank Cooperation Mechanism
The BRICS Interbank Cooperation Mechanism is an agreement between the central banks of the BRICS nations to promote financial stability and stimulate economic growth. The agreement was signed in 2013 and went into effect in 2015.
Under the agreement, the central banks of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa agreed to cooperate on a wide range of issues including:
-Developing a joint framework for addressing financial stability risks
-Enhancing payment and settlement systems
-Improving access to financing for small and medium enterprises
-Sharing knowledge and best practices on central banking operations
- The BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement
The BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) is an emergency funding mechanism created by the BRICS nations in 2014. The CRA is designed to provide financial assistance to member states in the event of a balance of payments crisis. The CRA is funded by contributions from each of the BRICS nations, and the total size of the fund is currently $100 billion.
The CRA is similar to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), but with a few key differences. First, the CRA is not open to all nations, but only to the BRICS nations. Second, the CRA is not centrally managed by a single institution, but is instead governed by a board of directors representing each of the BRICS nations. Third, the CRA does not impose conditionality on its loans, meaning that member states are not required to implement economic reforms in order to receive financial assistance.
The CRA has been criticized by some for being a tool of the BRICS nations, and not of the global economy. However, the CRA has been praised by others for its flexibility and for its willingness to provide assistance to countries in need without imposing harsh conditions.
- The BRICS Post-2015 Development Agenda
The BRICS Post-2015 Development Agenda is a set of 8 goals that the group of nations known as the BRICS have committed to working towards. The goals are:
- End poverty in all its forms everywhere
- End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
- Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
- Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
- Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
- Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all
- Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
The BRICS Post-2015 Development Agenda was formulated at the 7th BRICS summit in 2015, and is seen as a successor to the Millennium Development Goals. The Agenda is noteworthy for its focus on poverty alleviation, sustainable development, and global cooperation.
- The BRICS in the global economy
The five BRICS countries are Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa. They are all emerging economies with large populations and rapidly growing economies.
The BRICS countries have been working together since 2006, when they first met at a summit in Yekaterinburg, Russia. Since then, they have held annual summits, with the most recent one taking place in Xiamen, China in September 2017.
The BRICS countries are some of the most important emerging economies in the world. They are all members of the G20, and together they account for over 40% of the world’s population and more than 20% of the world’s GDP.
The BRICS countries are important trading partners for each other. China is the largest trading partner for Brazil, Russia and South Africa, and the second largest for India. Trade between the BRICS countries totaled $624 billion in 2016, and is expected to grow to $8 trillion by 2020.
The BRICS countries are also working together on a number of other initiatives. They have established the New Development Bank, which is intended to provide financing for infrastructure projects in the BRICS countries. They are also working on a BRICS rating agency, which will provide an alternative to the existing rating agencies like Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s.
- The future of the BRICS
The BRICS bloc of countries – Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – has seen significant growth in recent years, with many experts predicting that the group will continue to rise in prominence on the global stage. Here are 10 reasons why the future looks bright for the BRICS bloc:
-
The BRICS countries are home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies.
-
The BRICS bloc has a combined population of over 3 billion people – which is around 40% of the world’s population.
-
The BRICS countries are home to a growing middle class which is increasingly driving economic growth.
-
The BRICS bloc has a combined GDP of over US$16 trillion – which is around 20% of the world’s GDP.
-
The BRICS countries are home to some of the world’s largest companies, such as Petrobras, Gazprom, Sberbank, Alibaba and Tencent.
-
The BRICS bloc has a strong base of natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, iron ore and gold.
-
The BRICS bloc has a growing pool of highly-skilled workers and professionals.
-
The BRICS countries are investing heavily in infrastructure development.
-
The BRICS bloc is increasingly playing a key role in global affairs.
-
The future looks bright for the BRICS bloc.
References
- “What are the BRICS Countries?”. WorldAtlas.com.
- “The BRICS Bank”. The Economist.
- “What are the BRICS?”. CNBC.
- “What is the difference between the BRICS and the G20?”. Quora.
- “What do the BRICS really have in common?”. The Guardian.