-
2022年11月,美国国防部长劳埃德-奥斯汀访问印尼,讨论购买36架美国战斗机,但离开时没有达成协议。
-
几天前,印尼和中国承诺恢复联合军事演习。- 在美国和中国争夺亚洲影响力的地缘政治斗争中,印度尼西亚是一个重要的奖品。
-
该国的战略位置,有17,000个岛屿,横跨一条重要的海上通道,使其成为双方准备在台湾问题上可能发生冲突时的防卫必需品。
-
中国一直在印度尼西亚进行大量投资,以赢得民众的支持。
-
这包括开发世界上最大的镍矿,以及加快Covid-19疫苗的运输速度。
-
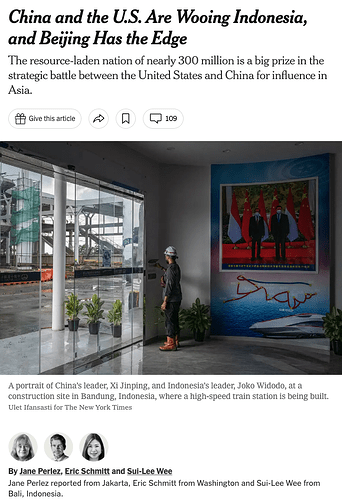
中国也一直是印尼推动基础设施建设的主要合作伙伴,如建造高速列车,尽管它迟到且超出预算。
-
总的来说,中国在向印尼示好方面取得了成功,并且似乎在这一关系中占据了优势。
-
2022年前九个月,中国在印度尼西亚投资了50亿美元。
-
美国在同一时期投资约20亿美元。
-
中国对印尼的投资是美国的两倍多。
-
这标志着中国正日益成为该地区的主要投资者。
-
中国官员在投资时不会像美国官员那样向印尼政府提出条件。
-
这使中国成为对印尼更有吸引力的合作伙伴。
-
作为回报,印尼在联合国投票支持中国在迫害维吾尔人问题上的立场。
-
印度尼西亚一直为中国不受限制地参与东南亚国家联盟所有10个成员国的经济活动而欢呼。
-
印度尼西亚总统佐科-维多多对中国领导人习近平有着特殊的亲和力,自2014年以来,他与习近平会面8次,而与美国前总统唐纳德-J-特朗普和拜登总统的会面只有4次。
-
佐科-维多多和习近平的政治利益汇合在一起,是印尼与中国建立热烈关系的关键因素。
-
维多多自担任总统以来的优先事项是基础设施,这也是习近平外交战略的基石。
-
在首次访问北京期间,维多多被带去体验了从北京到天津的高速列车,2015年10月,他签署了一项价值数十亿美元的协议,由中国在印尼建设基础设施。
-
印度尼西亚历史上有强烈的反华情绪,特别是在1965年,暴徒杀害了数十万人,包括华裔。
-
悲剧发生后,中国和印度尼西亚的关系被冻结了几十年。
-
中国现任驻印尼大使陆慷小心翼翼地避免用外交辞令和友好的社交媒体帖子来激起人们的怀疑。
-
1955年,中国总理周恩来访问印度尼西亚,试图建立外交关系,之后两国之间的紧张关系爆发。
-
中国已成为印度尼西亚的第一大贸易伙伴、第一大外国投资者和第一大国际游客来源国。
-
中国公司Tsingshan在该国的镍矿开采中占主导地位,中国还在建造燃煤发电站和加工原镍。
-
印度尼西亚能够确保中国制造的疫苗的早期供应。
-
中国制造的疫苗Sinovac被宣布为清真认证的疫苗。
-
中国和印度尼西亚的关系并非没有挑战,特别是关于从雅加达到万隆的88英里、55亿美元的高速列车的建设。
-
该项目最初承诺在2019年完成,但现在已经晚了三年,成本超支可能高达19亿美元。
-
印尼政府和中国政府正在讨论的一项再融资交易可能会导致中国将其在该铁路的所有权从40%增加到60%。
-
11月20国集团会议期间的试运行被取消,从中国运来的闪亮的新车厢被闲置在一个机库里。
-
印度尼西亚在与美国和中国打交道时很谨慎,试图在这两个大国之间保持中立。
-
拜登政府曾提议用核动力潜艇武装澳大利亚,印尼强烈反对这一计划,因为其水域有可能需要在台湾冲突中使用。
-
印度尼西亚已经宣布致力于在其领土周围建立一个无核区,并表示在美国和中国之间的台湾冲突中保持中立。
-
印度尼西亚外交部正在领导该国的谨慎做法,确保不激怒北京。
-
印度尼西亚的中立性给美国在亚洲对抗中国的努力带来了挑战。
-
在争夺台湾的战争中,对印尼基地的军事准入将是美国军队的一大优势,但这不可能发生。
-
去年8月,印尼参加了与美国军队的多国演习,但不太可能购买美国武器来替代其老化的俄罗斯武器。
-
印度尼西亚最近从法国购买了42架 "阵风 "战斗机,并决定出于预算原因不从美国购买F-15战斗机。
-
美国的努力只换来了印尼军事学生在美国的额外培训项目。印尼的军事学生也在俄罗斯和中国接受训练。
-
In November, U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd J. Austin III visited Indonesia to discuss buying 36 American fighter jets, but left without an agreement.
-
Days earlier, Indonesia and China pledged to resume joint military exercises. - Indonesia is a big prize in the geopolitical battle between the U.S. and China for influence in Asia.
-
The country’s strategic location, with 17,000 islands straddling a vital sea lane, makes it a defensive necessity for both sides as they prepare for a possible conflict over Taiwan.
-
China has been investing heavily in Indonesia in order to win over the populace.
-
This includes developing the world’s largest nickel deposits, as well as speeding up Covid-19 vaccine shipments.
-
China has also been a major partner in Indonesia’s infrastructure push, such as building a high-speed train, although it was late and over budget.
-
Overall, China has been successful in wooing Indonesia and appears to have the edge in the relationship.
-
China invested $5 billion in Indonesia in the first nine months of 2022.
-
US invested around $2 billion in the same time period.
-
China’s investment is more than double that of the US in Indonesia.
-
This signifies that China is increasingly becoming the main investor in the region.
-
Chinese officials do not dictate conditions to the Indonesian government when investing, unlike American officials.
-
This has made China a more attractive partner for Indonesia.
-
In return, Indonesia has voted in favor of China’s position at the United Nations on the persecution of Uyghurs.
-
Indonesia is a consistent cheerleader for China’s untrammeled economic involvement in all 10 member nations of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
-
Indonesian President Joko Widodo has had a special affinity for China’s leader, Xi Jinping, meeting him eight times since 2014 compared to four times with the former US president Donald J. Trump and President Biden.
-
The confluence of Joko Widodo’s and Xi Jinping’s political interests has been a key factor in Indonesia’s warm relationship with China.
-
Widodo’s priority since the start of his presidency has been infrastructure, which also has been a cornerstone of Xi Jinping’s diplomatic strategy.
-
During his first visit to Beijing, Widodo was taken to experience a high-speed train from Beijing to Tianjin, and in October 2015, he signed a multibillion-dollar deal for China to build an infrastructure in Indonesia.
-
Indonesian history is marked by strong anti-Chinese sentiment, particularly in 1965 when mobs killed hundreds of thousands of people, including ethnic Chinese.
-
Relations between China and Indonesia were frozen for decades following the tragedy.
-
China’s current ambassador to Indonesia, Lu Kang, is careful to not stoke suspicions with diplomatic niceties and friendly social media posts.
-
In 1955, China’s Prime Minister Zhou Enlai visited Indonesia in an attempt to build diplomatic relations, before tensions between the two countries erupted.
-
China has become the No. 1 trading partner, No. 1 foreign investor, and No. 1 source of international tourists in Indonesia.
-
Chinese company, Tsingshan, dominates the country’s nickel mining and China is also building coal-fired power stations and processing raw nickel.
-
Indonesia was able to secure early supplies of Chinese-made vaccines.
-
Sinovac, the Chinese-made vaccine, was declared halal-certified.
-
China and Indonesia have a relationship that is not without challenges, particularly concerning the construction of an 88-mile, $5.5 billion high-speed train from Jakarta to Bandung.
-
The project was initially promised to be completed by 2019, but it is now three years late and the cost overrun could be as much $1.9 billion.
-
A refinancing deal that the Indonesian government and Beijing are discussing is likely to result in China increasing its ownership stake in the rail from 40 percent to 60 percent.
-
The trial run to showcase the train during the Group of 20 meeting in November was canceled, and the shiny new carriages shipped from China sit idle in a hangar.
-
Indonesia is cautious in its dealings with the US and China, attempting to remain neutral between the two powers.
-
The Biden administration had proposed to arm Australia with nuclear-powered submarines, a plan which Indonesia strongly opposed due to the potential of their waters needing to be used in a conflict over Taiwan.
-
Indonesia has declared its commitment to having a nuclear-free zone around its territory and has stated that it would remain neutral in a conflict over Taiwan between the US and China.
-
The Indonesian Ministry of Foreign Affairs is leading the country’s cautious approach, ensuring that it does not anger Beijing.
-
Indonesia’s neutrality has created a challenge for the US in its efforts to counter China in Asia.
-
Military access to Indonesia’s bases would be a major asset to US forces in a war over Taiwan, but this is not likely to happen.
-
Indonesia participated in a multinational exercise with US forces last August, but is unlikely to purchase US weapons as replacements for its aging Russian weapons.
-
Indonesia recently bought 42 Rafale fighter jets from France, and decided against purchasing F-15 fighter jets from the US for budgetary reasons.
-
The US was only able to gain additional training programs in the US for Indonesian military students in exchange for its efforts. Indonesian military students also train in Russia and China.
链接:China and the U.S. Are Wooing Indonesia, and Beijing Has the Edge - The New York Times